M01 - Unit 4 Design and implement a Virtual Network in Azure
Exercise scenario
Now you’re ready to deploy virtual networks in the Azure portal.
Consider the fictional organization Contoso Ltd, which is in the process of migrating infrastructure and applications to Azure. In your role as network engineer, you must plan and implement three virtual networks and subnets to support resources in those virtual networks.
Estimated time: 20 minutes
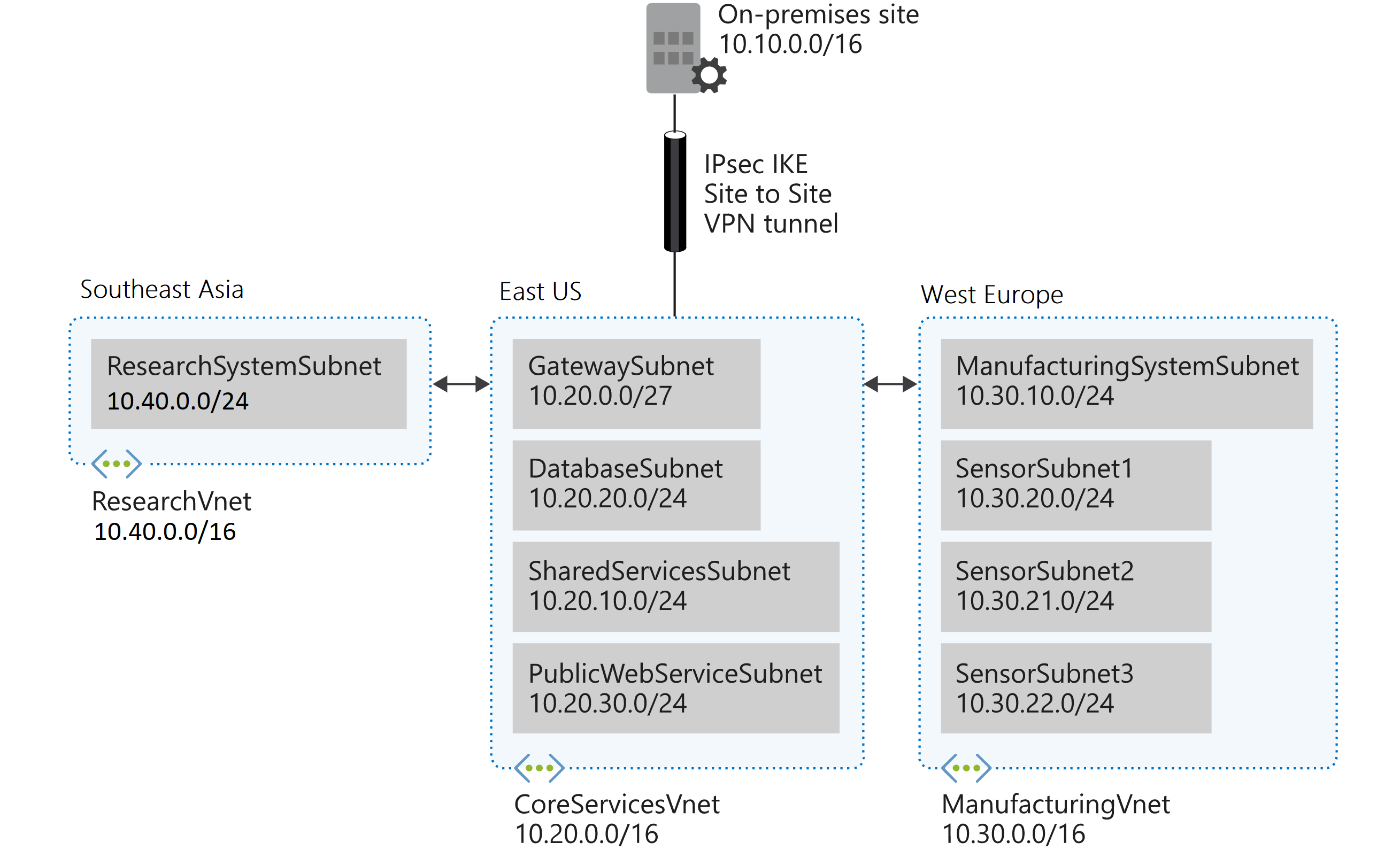
The CoreServicesVnet virtual network is deployed in the East US region. This virtual network will have the largest number of resources. It will have connectivity to on-premises networks through a VPN connection. This network will have web services, databases, and other systems that are key to the operations of the business. Shared services, such as domain controllers and DNS also will be located here. A large amount of growth is anticipated, so a large address space is necessary for this virtual network.
The ManufacturingVnet virtual network is deployed in the West Europe region, near the location of your organization’s manufacturing facilities. This virtual network will contain systems for the operations of the manufacturing facilities. The organization is anticipating a large number of internal connected devices for their systems to retrieve data from, such as temperature, and will need an IP address space that it can expand into.
The ResearchVnet virtual network is deployed in the Southeast Asia region, near the location of the organization’s research and development team. The research and development team uses this virtual network. The team has a small, stable set of resources that is not expected to grow. The team needs a small number of IP addresses for a few virtual machines for their work.
You will create the following resources:
| Virtual Network | Region | Virtual network address space | Subnet | Subnet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoreServicesVnet | East US | 10.20.0.0/16 | ||
| GatewaySubnet | 10.20.0.0/27 | |||
| SharedServicesSubnet | 10.20.10.0/24 | |||
| DatabaseSubnet | 10.20.20.0/24 | |||
| PublicWebServiceSubnet | 10.20.30.0/24 | |||
| ManufacturingVnet | West Europe | 10.30.0.0/16 | ||
| ManufacturingSystemSubnet | 10.30.10.0/24 | |||
| SensorSubnet1 | 10.30.20.0/24 | |||
| SensorSubnet2 | 10.30.21.0/24 | |||
| SensorSubnet3 | 10.30.22.0/24 | |||
| ResearchVnet | Southeast Asia | 10.40.0.0/16 | ||
| ResearchSystemSubnet | 10.40.0.0/24 |
These virtual networks and subnets are structured in a way that accommodates existing resources yet allows for projected growth. Let’s create these virtual networks and subnets to lay the foundation for our networking infrastructure.
Job skills
In this exercise, you will:
- Task 1: Create the Contoso resource group
- Task 2: Create the CoreServicesVnet virtual network and subnets
- Task 3: Create the ManufacturingVnet virtual network and subnets
- Task 4: Create the ResearchVnet virtual network and subnets
- Task 5: Verify the creation of VNets and Subnets
Task 1: Create the Contoso resource group
-
Go to Azure portal.
-
On the home page, under Azure services, select Resource groups.
-
In the Resource groups, select + Create.
-
Use the information in the following table to create the resource group.
Tab Option Value Basics Resource group ContosoResourceGroup Region (US) East US Tags No changes required Review + create Review your settings and select Create -
In Resource groups, verify that ContosoResourceGroup appears in the list.
Task 2: Create the CoreServicesVnet virtual network and subnets
-
On the Azure portal home page, navigate to the Global Search bar and search Virtual Networks and select virtual networks under services.
-
Select Create on the Virtual networks page.
-
Use the information in the following table to create the CoreServicesVnet virtual network.
Remove or overwrite the default IP Address space.
Tab Option Value Basics Resource Group ContosoResourceGroup Name CoreServicesVnet Region (US) East US IP Addresses IPv4 address space 10.20.0.0/16 -
Use the information in the following table to create the CoreServicesVnet subnets.
-
To begin creating each subnet, select + Add subnet. To finish creating each subnet, select Add. If needed, Edit (pencil icon) or Delete the default subnet.
Subnet Option Value GatewaySubnet Subnet purpose Virtual Network Gateway Subnet name GatewaySubnet Subnet address range 10.20.0.0/27 SharedServicesSubnet Subnet name SharedServicesSubnet Subnet address range 10.20.10.0/24 DatabaseSubnet Subnet name DatabaseSubnet Subnet address range 10.20.20.0/24 PublicWebServiceSubnet Subnet name PublicWebServiceSubnet Subnet address range 10.20.30.0/24 -
To finish creating the CoreServicesVnet and its associated subnets, select Review + create.
-
Verify your configuration passed validation, and then select Create.
-
Repeat steps 1 -8 for each VNet based on the tables below
Task 3: Create the ManufacturingVnet virtual network and subnets
| Tab | Option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Basics | Resource Group | ContosoResourceGroup |
| Name | ManufacturingVnet | |
| Region | (Europe) West Europe | |
| IP Addresses | IPv4 address space | 10.30.0.0/16 |
| Subnet | Option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| ManufacturingSystemSubnet | Subnet name | ManufacturingSystemSubnet |
| Subnet address range | 10.30.10.0/24 | |
| SensorSubnet1 | Subnet name | SensorSubnet1 |
| Subnet address range | 10.30.20.0/24 | |
| SensorSubnet2 | Subnet name | SensorSubnet2 |
| Subnet address range | 10.30.21.0/24 | |
| SensorSubnet3 | Subnet name | SensorSubnet3 |
| Subnet address range | 10.30.22.0/24 |
Task 4: Create the ResearchVnet virtual network and subnets
| Tab | Option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Basics | Resource Group | ContosoResourceGroup |
| Name | ResearchVnet | |
| Region | Southeast Asia | |
| IP Addresses | IPv4 address space | 10.40.0.0/16 |
| Subnet | Option | Value |
|---|---|---|
| ResearchSystemSubnet | Subnet name | ResearchSystemSubnet |
| Subnet address range | 10.40.0.0/24 |
Task 5: Verify the creation of VNets and Subnets
-
On the Azure portal home page, select All resources.
-
Verify that the CoreServicesVnet, ManufacturingVnet, and ResearchVnet are listed.
-
Select CoreServicesVnet.
-
In CoreServicesVnet, under Settings, select Subnets.
-
In CoreServicesVnet | Subnets, verify that the subnets you created are listed, and that the IP address ranges are correct.
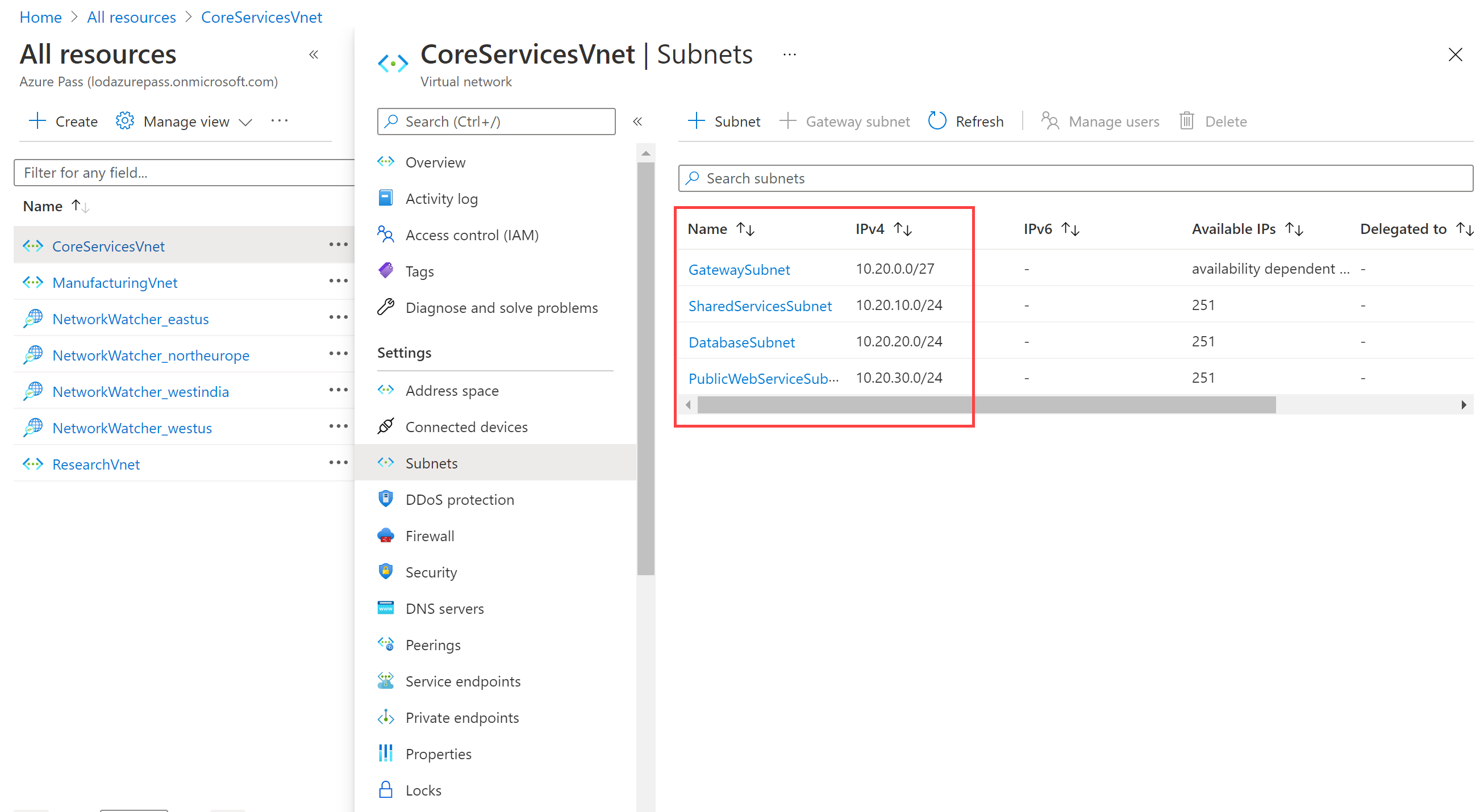
-
Repeat steps 3 - 5 for each VNet.
Extend your learning with Copilot
Copilot can assist you in learning how to use the Azure scripting tools. Copilot can also assist in areas not covered in the lab or where you need more information. Open an Edge browser and choose Copilot (top right) or navigate to copilot.microsoft.com. Take a few minutes to try these prompts.
- Can you provide an example of how the 10.30.0.0/16 IP address is used in a real-world scenario?
- What is the Azure PowerShell command to create a virtual network called CoreServicesVnet in the East (US) region. The virtual network should use the 10.20.0.0/16 IP address space.
- What is the Azure CLI command to create a virtual network called ManufacturingVnet in the West Europe region. The virtual network should use the 10.30.0.0/16 IP address space.
Learn more with self-paced training
- Design an IP addressing schema for your Azure deployment. In this module, identify the public and private IP addressing capabilities of Azure virtual networks.
- Introduction to Azure Virtual Networks. In this module, you learn how to design and implement Azure networking services. You learn about virtual networks, public and private IPs, DNS, virtual network peering, routing, and Azure Virtual NAT.
Key takeaways
- Azure Virtual Network is a service that provides the fundamental building block for your private network in Azure. An instance of the service (a virtual network) enables many types of Azure resources to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. Ensure nonoverlapping address spaces. Make sure your virtual network address space (CIDR block) doesn’t overlap with your organization’s other network ranges.
- All Azure resources in a virtual network are deployed into subnets within the virtual network. Subnets enable you to segment the virtual network into one or more subnetworks and allocate a portion of the virtual network’s address space to each subnet. Your subnets shouldn’t cover the entire address space of the virtual network. Plan ahead and reserve some address space for the future.